Data Presentation
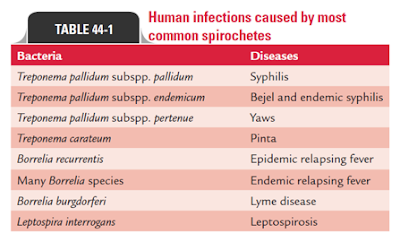
Data: is any observational collected in respect of any characteristic or event. Types of data: 1) Qualitative / quantitative data. 2) Discrete / continuous data. 3) Primary / secondary data. 4) Nominal / ordinal data. Principals of data presentation: a) To arrange data in order to create interest in reader’s mind. b) To present information in a compact and concise form without losing important details. c) To present data in a simple form to draw conclusion directly by viewing data. d) To present data in order to help in further statistical analysis. Types of presentation of data: Tabulation (making tables): is the most common method of presenting analyzed data which offers a useful means of presenting large amounts of detailed information in a small space. Tables can clarify text, provide visual relief, and serve as quick point of reference. To write table in a perfect way: 1) Tables should be numbered ex: table 1